What is the Metaverse?
-
May 06, 2023
Informational

Written By: Steven Shannon
On 28 October 2021, Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg announced the rebranding of their corporate name from Facebook to Meta, outlining their newfound goal of stepping into the virtual reality space, and immediately after, interest in the term Metaverse sharply rose. But the term was not coined by Meta; instead, it was author Neal Stephenson who first used it in his science fiction novel Snow Crash to envision, according to MIT Technology Review, “a computer-generated virtual word made possible by software and a worldwide fiber-optic network.” Since then, the Metaverse has been used to describe a virtual world that merges both physical reality and virtual reality.
The Metaverse
Referred to as “the next generation of the internet” by Meta chief business officer Marne Levine, the Metaverse is a change in how we interact with technologies. It reworks our current online experiences into immersive, interconnected, accessible digital spaces. These spaces can be accessed with all kinds of technology, VR headsets to phone screens, without regard for physical location. The Metaverse also takes immersion and interactivity to a whole new level, bringing co-presence into the digital world without limiting it to just 2D images and texts.
The blockchain and Web 3.0 technologies behind Metaverse will ensure that it is an open source, decentralized, and interoperable platform. An open source platform means that the creator or owner of the software has granted others the right to use, modify, and distribute the software and its source code. By having the platform be open source, it promotes diversity and allows more people to create Metaverse spaces and assets. A decentralized network uses multiple servers to store information. Each server is independent from another, and they all have a copy of the same data. This bolsters the security of the platform as information is only modified based on consensus from the group and as other servers hold backup information if one server fails. Blockchain technology is an example of a decentralized system that is used to hold proof of purchase and ownership of digital assets. An interoperable platform means that the user can take things in and out as they travel between virtual spaces, such as having the same avatar throughout all virtual spaces or not having to login to a new account for each virtual space.

Metaverse avatars. Source: https://jingculturecrypto.com/metaverse-interoperability-the-sandbox-season-3/
The Metaverse Market
The market for the Metaverse is expected to grow exponentially. In 2022, it was estimated that the global market stood at 65.5 billion USD. In 2023, it is expected to rise to 82 billion dollars. In the next 8 years, by 2030, the market is expected to grow up to 936.6 billion dollars.
Part of the growth of the market is due to the growing number of companies that are using the Metaverse right now. From gaming companies to art companies, the Metaverse is a great tool for them to expand their business and audience. For example, art auction houses Christie’s and Sotheby’s have opened art galleries in Metaverse to facilitate the selling of NFT artworks. Sotheby’s first Metaverse auction in 2021 of 53 NFTs brought in approximately 18.7 million USD.
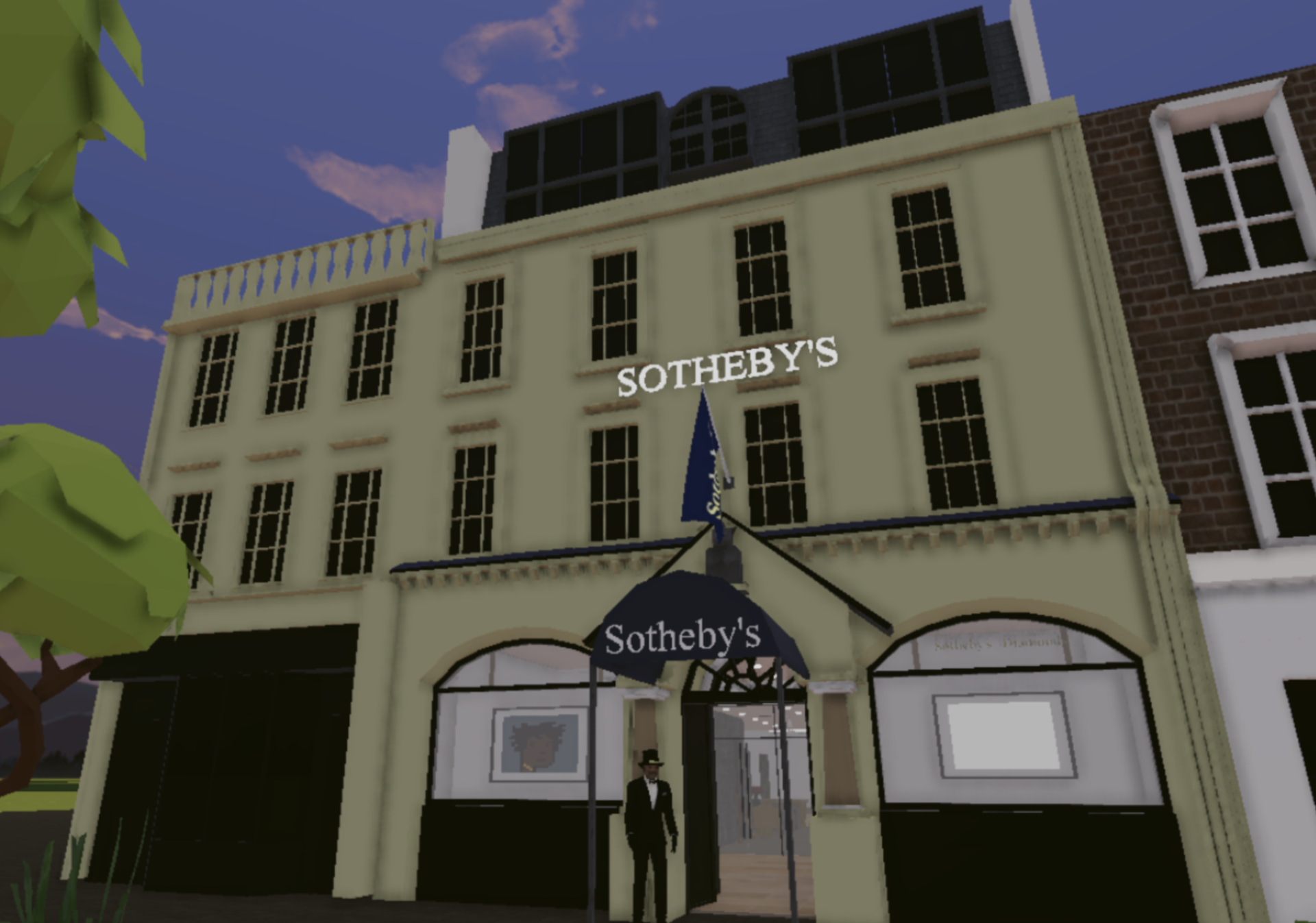

Sotheby’s art gallery in the Metaverse. Source: Decentraland
Capabilities and Features
As the Metaverse encompasses many changes in the way we interact with technology, it supports many features and is endlessly capable.
1.Enhanced Social Platform
First and foremost is that the platform is a virtual world meant to enhance social interaction. The Metaverse can hold a near-infinite number of digital spaces, and each space can be distinct from one another in purpose and design. Whether the digital space is an office for business conferences, a classroom for online learning, or a backyard for a small social gathering, there is no limit to the type and purpose of the digital space. Though this may seem redundant in comparison to our physical reality, this feature of virtual reality has many advantages over its physical counterpart. For one, users may enjoy the presence of others in a variety of environments while being in the comforts of their own home. Secondly, the Metaverse is not limited to physical space and capacity. This means that users can create as many unique spaces as they want for any purpose. This also means that the spaces can host large numbers of users.
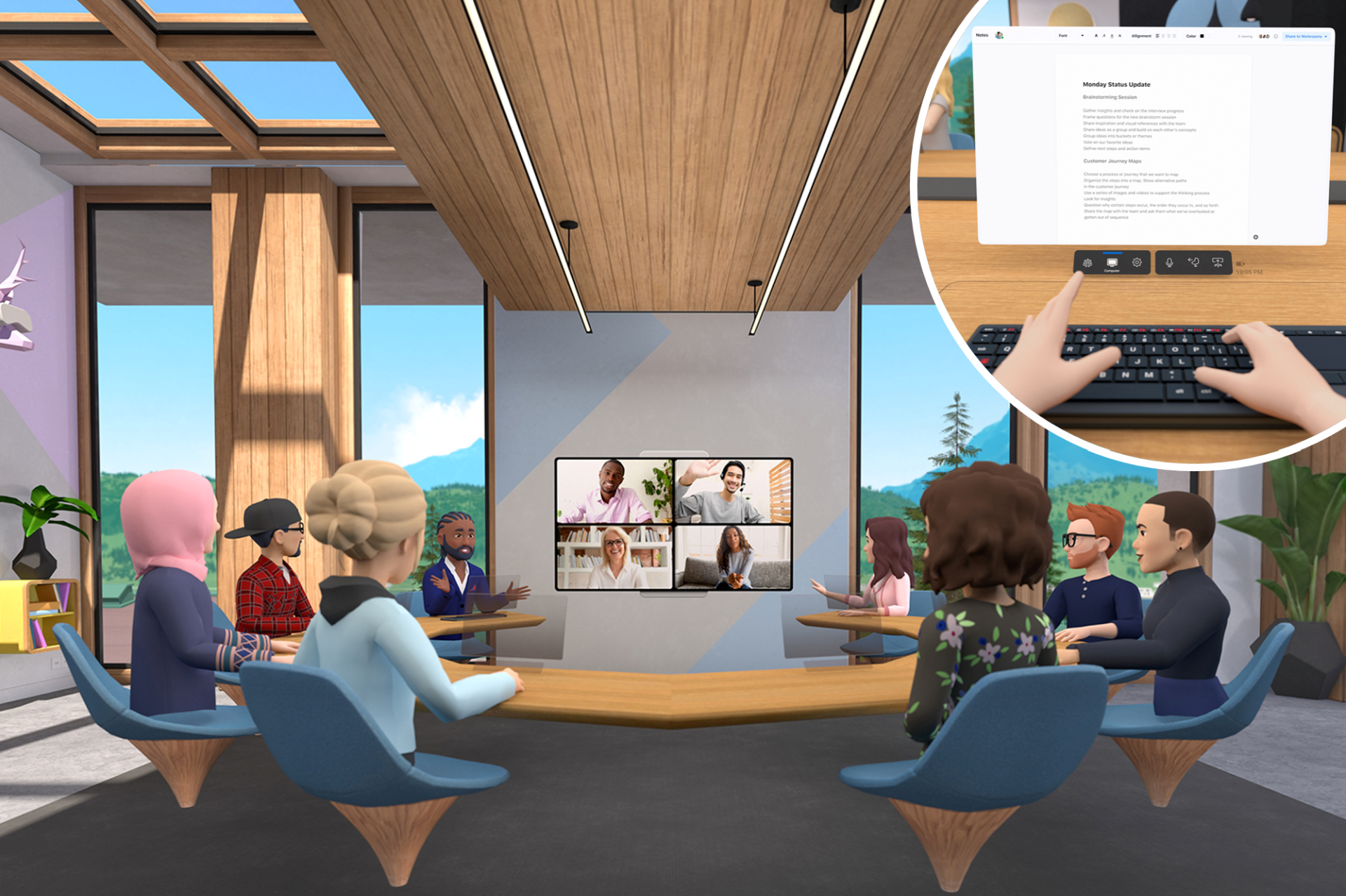

Business meeting conducted in Metaverse. Source: https://www.the-sun.com/tech/3502098/facebook-oculus-workroom-vr-virtual-reality-mark-zuckerberg-metaverse/
2. Security
Another feature of the Metaverse is its security. For starters, as an open source platform, the community can contribute to the security of the platform whenever they encounter a bug or glitch by submitting feedback or by fixing the code themselves. In addition, Metaverse relies on Web 3.0 and blockchain technologies to create a decentralized platform. Blockchain ensures data validity through proof of ownership for digital assets, meaning users’ virtual assets are safeguarded. Web 3.0 is a decentralized infrastructure, meaning that no one single authority has control over the entire Metaverse.
3. Shopping
A significant feature of the Metaverse is its integration of online shopping and e-commerce. Through augmented reality technologies, users have the option of trying out clothes, furniture, and so on before purchasing them in the physical reality. However, the Metaverse also incorporates another thriving economy: cryptocurrency and NFTs. With a digital wallet, users can store and exchange their cryptocurrency very easily, and with digital spaces, users can view, purchase, and display NFT assets.
Possible Concerns
With all these great benefits from joining the Metaverse, there are also some issues we may run into while using cyberspace.
1.Privacy
The Metaverse is hailed as the next generation of the Internet, and already, in our current Internet, there are data and information privacy concerns. For example, companies can already acquire data on what consumers search in their search engines. With the advancement of Metaverse technology, VR headsets may include eye-tracking technology and haptic sensors, and companies may be able to access data from these sensors. With this data, companies can potentially track where we are looking, how long we are looking, our physical reactions, and so on.
2. Health
Since we began widespread use of handheld mobile devices and the Internet, there have been many stories of how constant use had led to health complications, though research does not provide conclusive evidence corroborating those stories. However, by strapping multiple technologies to our bodies to access and interact with the Metaverse, we may be opening ourselves up to health concerns.
Aside from physical health, virtual reality also poses a risk to mental health. Currently, there are known conditions of VR “hangovers” and post-VR sadness where some experience sadness after enjoying an immersive, beautiful virtual world and then returning to the real world. This could lead to an addiction or an escape from the real world.
3. Access
While the goal of the Metaverse is to be as accessible as possible, the quality of the immersion and experience relies on the technology used to access the digital world. A low-quality VR headset may not display the world as nicely as a high-quality headset, and this creates an inequality in the experience. This concern is heightened if the developers of the digital spaces use high quality technology as the standard for potential users as other parties are overlooked in the development process.
Despite the concerns raised, the Metaverse has many benefits that outweigh the disadvantages. From holding virtual concerts to showcasing art, many individual creators and companies, like Justin Bieber or ANGLtheARTIST, are using the Metaverse to host virtual worlds to expand their business. As an emerging technology, the Metaverse will become a game-changer for all digital interactions.
Stay tuned as #MeetArts will be launching our Metaverse gallery in the second half of 2023!
References:
LearnWAB Courses (https://learn.wablab.sg/course/what-is-the-metaverse-by-meta)
https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2021/oct/28/facebook-name-change-rebrand-meta
https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=today%205-y&geo=SG&q=metaverse&hl=en
https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/02/08/1044732/metaverse-history-snow-crash/
https://www.wired.com/story/what-is-the-metaverse/
https://blog.nextearth.io/capabilities-of-the-metaverse-98fc8c43d396
https://chainyard.com/web3/the-metaverse-key-features-and-challenges/
https://www.spiceworks.com/tech/artificial-intelligence/articles/what-is-metaverse/#_002
https://bernardmarr.com/7-important-problems-disadvantages-of-the-metaverse/
https://metarficial.com/challenges-disadvantages-metaverse/
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1295784/metaverse-market-size/


 PREVIOUS ARTICLE
PREVIOUS ARTICLE